Radiology in veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine in which doctors use imaging technology to visualize the interior of a pet’s body using various forms of radiation and non-radiation techniques. At Hickory Veterinary and Specialty Hospital we utilize an array of imaging technologies such as:
- Digital Radiography
- Digital Dental Radiography
- State of the art 64-slice CT Scanner
- MRI - Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Ultrasound
- Endoscopy (diagnostic technology)
Radiography
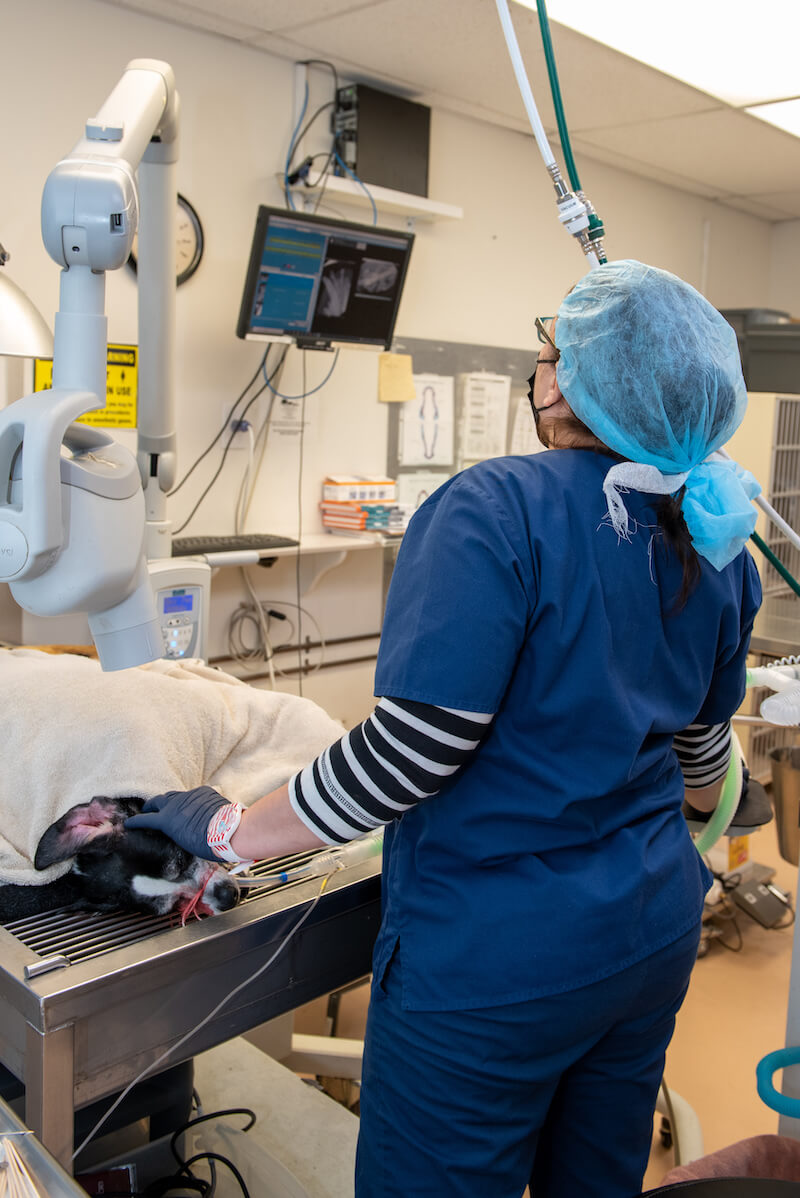 Radiography can be thought of as ‘X ray photography’. The images that are formed by passing an X ray beam through a section of a patient’s body are recorded either on film or some form of digital media. Generally, the images recorded on film are viewed as transparencies on a lighted view-box or illuminator and the digital images are viewed on computer displays.
Radiography can be thought of as ‘X ray photography’. The images that are formed by passing an X ray beam through a section of a patient’s body are recorded either on film or some form of digital media. Generally, the images recorded on film are viewed as transparencies on a lighted view-box or illuminator and the digital images are viewed on computer displays.
Digital Radiography
The general trend in the world is a transition from film-based to digital radiography. Hickory Veterinary and Specialty Hospital utilizes digital radiography for advanced diagnostics.
Digital Radiography, otherwise known as DR, is very similar to a digital camera. It gives us the ability to have “instant x-rays”. Just as a digital camera no longer uses film to capture pictures, DR no longer requires x-ray film. Instead, our DR unit uses a laptop computer to capture our x-ray image. This allows us to obtain clear, superior images in a matter of moments. We no longer have to develop the x-ray and instead we are able to view the x-ray instantly. With the x-ray displayed on the laptop screen, we have the ability to magnify and adjust the image, giving us greater detail and accuracy for our diagnosis and treatment. In addition to improved quality and reduced processing time, DR allows us to store images on CDs or thumb drives and to share with colleagues electronically.
Some of the specific advantages of digital radiography include:
- Elimination of chemical processing of films
- Reduced space requirements for storage of images
- Ability to apply digital image processing to optimize image quality and visibility of pathologic conditions
- Rapid transmission of images to other locations for viewing by physicians.
CT (Computed Tomography)
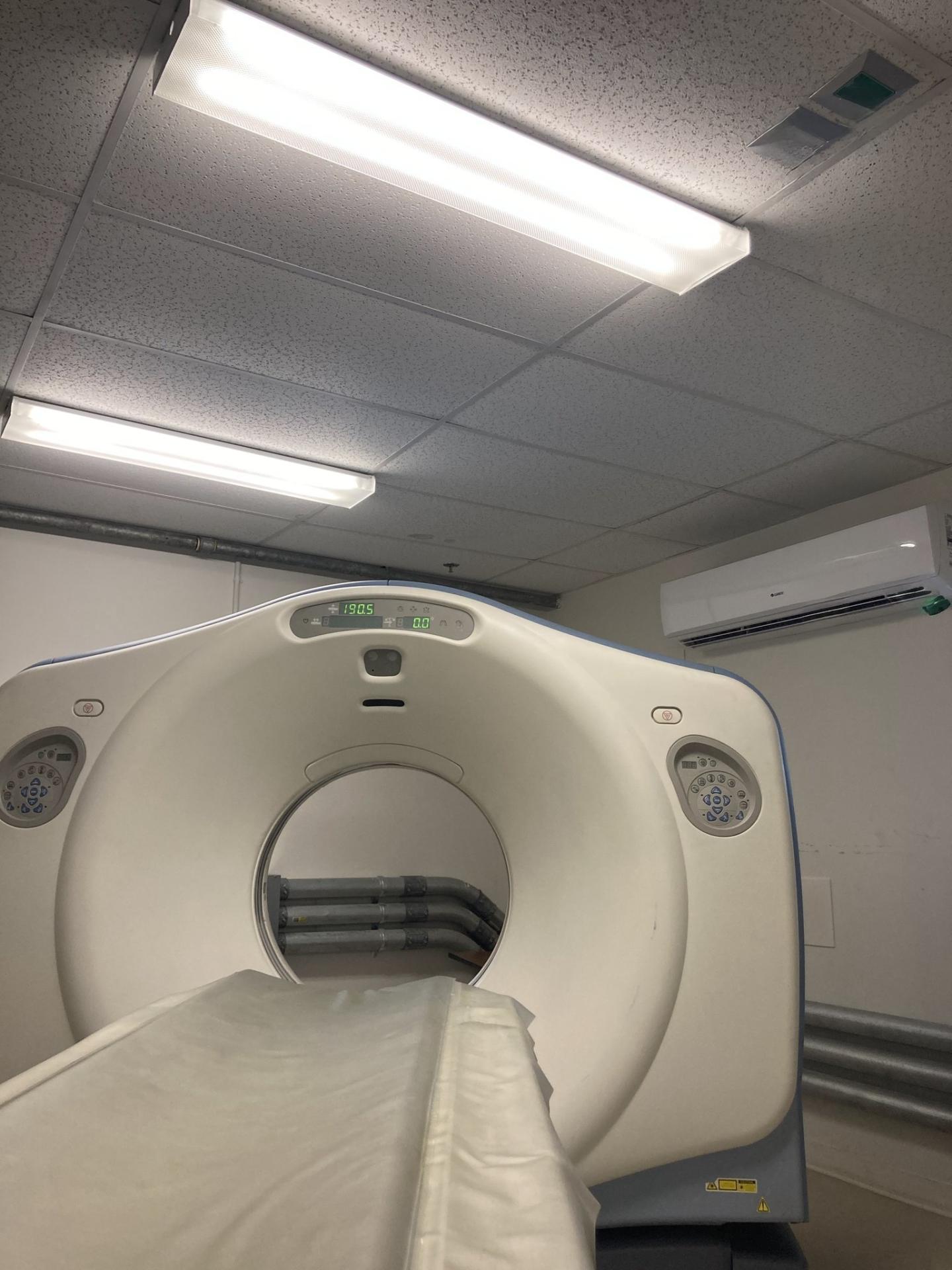 A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs and blood vessels. CT scans are more detailed than standard x-rays.
A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs and blood vessels. CT scans are more detailed than standard x-rays.
We offer the state-of-the-art 64-slice CT scanner with technology that represents an innovation of great magnitude that allows for information to be obtained faster and more accurately than before.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological process of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. There is no radiation exposure with magnetic resonance imaging.
Our MRI trailer is located on the premises for easy and safe access. Our board certified neurologist reviews the images and consults with you on MRI findings and medical plan.
Endoscopy
The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. One of the benefits to all types of endoscopy, is that this procedure is minimally invasive, using open cavities (mouth, nose, urethra or rectum) to insert a tube with a small camera into the anesthetized patient and does not involve the use of radiation. This small camera allow us to visualize and take biospies (samples) of areas of interest. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ to be examined. There are many types of endoscopies.
- Arthoscopy - scoping of joints
- Bronchoscopy - scoping of trachea and the lungs
- Colonoscopy - scoping of entire length of the colon and large intestines
- Cystoscopy - scoping of the inside of the bladder
- Esophagoscopy - scoping of the esophagus
- Gastroscopy - scoping of the stomach and duodenum which is the beginning of the small intestine, foreign body retrieval
- Rhinoscopy - scoping of the nasal cavity
Ultrasound
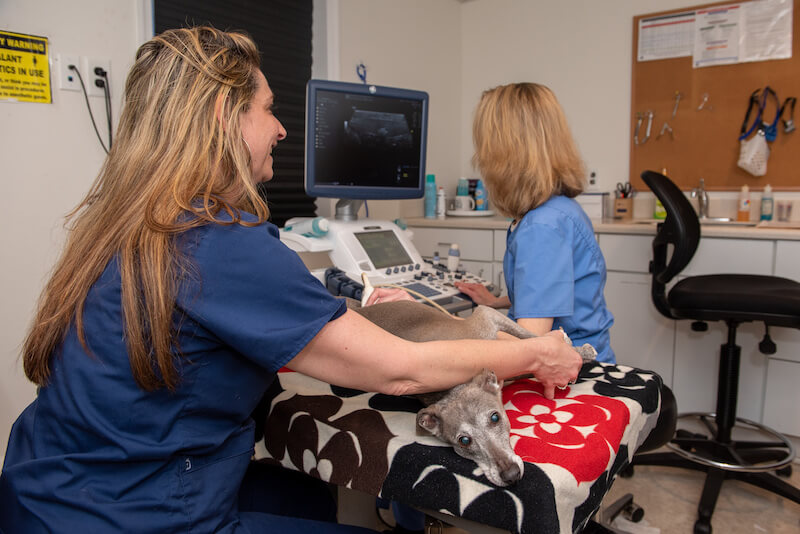 Ultrasound is a painless imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images of soft tissue, organs, blood flow and other anatomy. It is noninvasive and does not involve the use of radiation. Ultrasound can be used to diagnose illness, characterize anatomy, and guide the direction of biopsy or other diagnostic sampling.
Ultrasound is a painless imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images of soft tissue, organs, blood flow and other anatomy. It is noninvasive and does not involve the use of radiation. Ultrasound can be used to diagnose illness, characterize anatomy, and guide the direction of biopsy or other diagnostic sampling.
The Ultrasound Procedure
While most pets require no sedation and lay quietly for the procedure, especially nervous or wiggly patients may need sedation to enable a thorough examination. Sedation or brief anesthesia is usually employed if a biopsy or needle aspirate procedure is performed.
The procedure involves placing your pet on our ultrasound table and held comfortably while the doctor performs the ultrasound using ultrasound gel.
The doctor will review the findings with you and with your veterinarian.
